
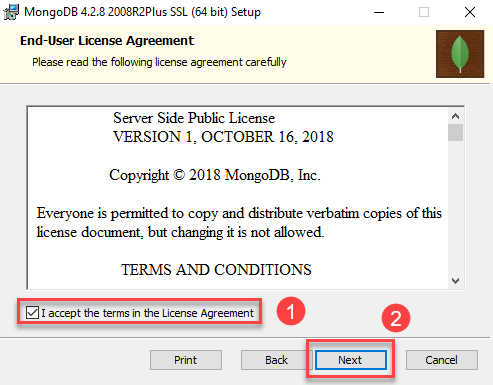
Change or modify the permission of log and data directories for mongodb user if necessary.įollowing commands to start|enable|restart|status|stop "mongod service". var/log/mongodb/mongod.log -> Log fileīy default MongoDB runs with "mongodb" user. Step 5: Directories and Configuration filesįollowings are the data and log file location if the MongoDB is installed using package manager (Click on picture to enlarge it). That is, if you change the configuration file while the MongoDB instance is running, you must restart the instance for the changes to take effect.$ sudo echo "deb bionic/mongodb-org/4.4 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt//mongodb-org-4.4.listĮxecute the following command to install MongoDB stable version (Click on picture to enlarge it). These settings (such as the data directory and log directory specifications) take effect upon startup. The official MongoDB package includes a configuration file ( /etc/nf). If you change the user that runs the MongoDB process, you must also modify the permission to the data and log directories to give this user access to these directories. The data directory /var/lib/mongo and the log directory /var/log/mongodb are created during the installationīy default, MongoDB runs using the mongodb user account. The data directory /var/lib/mongodb and the log directory /var/log/mongodb are created during the installation. Starting in MongoDB 4.4, a startup error is generated if the ulimit value for number of open files is under 64000. See UNIX ulimit Settings for the recommended settings for your platform. These limits may negatively impact MongoDB operation, and should be adjusted.
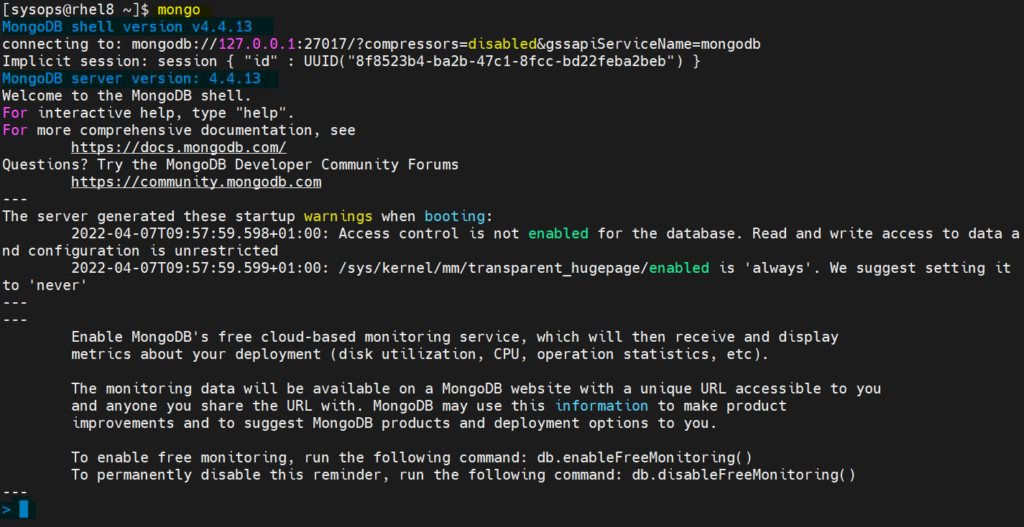
Most Unix-like operating systems limit the system resources that a process may use. You can use the mongo shell to query and update data as well as perform administrative operations also as a way for developers to test queries and operations directly with the database. The mongo shell is an interactive JavaScript interface to MongoDB. MongoDB uses the mongo shell to interact with MongoDB.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
